Classroom English-Grammar-Past Continuous

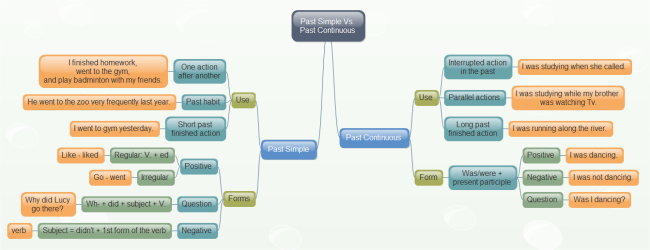
Past Continuous
FORM
[was/were + present participle]
Examples:

- You were studying when she called.
- Were you studying when she called?
- You were not studying when she called.

USE 1 Interrupted Action in the Past
 Use the Past Continuous to indicate that a longer action in the past was interrupted. The interruption is usually a shorter action in the Simple Past. Remember this can be a real interruption or just an interruption in time.
Use the Past Continuous to indicate that a longer action in the past was interrupted. The interruption is usually a shorter action in the Simple Past. Remember this can be a real interruption or just an interruption in time.
Examples:
- I was watching TV when she called.
- When the phone rang, she was writing a letter.
- While we were having the picnic, it started to rain.
- What were you doing when the earthquake started?
- I was listening to my iPod, so I didn’t hear the fire alarm.
- You were not listening to me when I told you to turn the oven off.
- While John was sleeping last night, someone stole his car.
- Sammy was waiting for us when we got off the plane.
- While I was writing the email, the computer suddenly went off.
- A: What were you doing when you broke your leg? B: I was snowboarding.
USE 2 Specific Time as an Interruption
 In USE 1, described above, the Past Continuous is interrupted by a shorter action in the Simple Past. However, you can also use a specific time as an interruption.
In USE 1, described above, the Past Continuous is interrupted by a shorter action in the Simple Past. However, you can also use a specific time as an interruption.
Examples:
- Last night at 6 PM, I was eating dinner.
- At midnight, we were still driving through the desert.
- Yesterday at this time, I was sitting at my desk at work.
IMPORTANT
In the Simple Past, a specific time is used to show when an action began or finished. In the Past Continuous, a specific time only interrupts the action.
Examples:
- Last night at 6 PM, I ate dinner. I started eating at 6 PM.
- Last night at 6 PM, I was eating dinner. I started earlier; and at 6 PM, I was in the process of eating dinner.
USE 3 Parallel Actions
 When you use the Past Continuous with two actions in the same sentence, it expresses the idea that both actions were happening at the same time. The actions are parallel.
When you use the Past Continuous with two actions in the same sentence, it expresses the idea that both actions were happening at the same time. The actions are parallel.
Examples:
- I was studying while he was making dinner.
- While Ellen was reading, Tim was watching television.
- Were you listening while he was talking?
- I wasn’t paying attention while I was writing the letter, so I made several mistakes.
- What were you doing while you were waiting?
- Thomas wasn’t working, and I wasn’t working either.
- They were eating dinner, discussing their plans, and having a good time.
USE 4 Atmosphere
In English, we often use a series of parallel actions to describe the atmosphere at a particular time in the past.
Example:
- When I walked into the office, several people were busily typing, some were talking on the phones, the boss was yelling directions, and customers were waiting to be helped. One customer was yelling at a secretary and waving his hands. Others were complaining to each other about the bad service.
USE 5 Repetition and Irritation with “Always”
 The Past Continuous with words such as “always” or “constantly” expresses the idea that something irritating or shocking often happened in the past. The concept is very similar to the expression “used to” but with negative emotion. Remember to put the words “always” or “constantly” between “be” and “verb+ing.”
The Past Continuous with words such as “always” or “constantly” expresses the idea that something irritating or shocking often happened in the past. The concept is very similar to the expression “used to” but with negative emotion. Remember to put the words “always” or “constantly” between “be” and “verb+ing.”
Examples:
- She was always coming to class late.
- He was constantly talking. He annoyed everyone.
- I didn’t like them because they were always complaining.
While vs. When
Clauses are groups of words which have meaning, but are often not complete sentences. Some clauses begin with the word “when” such as “when she called” or “when it bit me.” Other clauses begin with “while” such as “while she was sleeping” and “while he was surfing.” When you talk about things in the past, “when” is most often followed by the verb tense Simple Past, whereas “while” is usually followed by Past Continuous. “While” expresses the idea of “during that time.” Study the examples below. They have similar meanings, but they emphasize different parts of the sentence.
Examples:
- I was studying when she called.
- While I was studying, she called.

REMEMBER Non-Continuous Verbs / Mixed Verbs
It is important to remember that Non-Continuous Verbs cannot be used in any continuous tenses. Also, certain non-continuous meanings forMixed Verbs cannot be used in continuous tenses. Instead of using Past Continuous with these verbs, you must use Simple Past.
Examples:
Note: with verbs not normally used in the continuous form, the simple past is used.
- Jane was being at my house when you arrived. Not Correct
- Jane was at my house when you arrived. Correct
FUNCTIONS OF THE PAST CONTINUOUS
The past continuous describes actions or events in a time before now, which began in the past and is still going on at the time of speaking. In other words, it expresses an unfinished or incomplete action in the past. It is used:- Often, to describe the background in a story written in the past tense, e.g. “The sun was shining and the birds were singing as the elephant came out of the jungle. The other animals were relaxing in the shade of the trees, but the elephant moved very quickly. She was looking for her baby, and she didn’t notice the hunter who was watching her through his binoculars. When the shot rang out, she was running towards the river…”
- to describe an unfinished action that was interrupted by another event or action, e.g. “I was having a beautiful dream when the alarm clock rang.”
- to express a change of mind: e.g. “I was going to spend the day at the beach but I’ve decided to get my homework done instead.”
- with ‘wonder’, to make a very polite request: e.g. “I was wondering if you could baby-sit for me tonight.”
EXAMPLES
- They were waiting for the bus when the accident happened.
- Caroline was skiing when she broke her leg.
- When we arrived he was having a bath.
- When the fire started I was watching television.
FORMING THE PAST CONTINUOUS
The past continuous of any verb is composed of two parts : the past tense of the verb “to be” (was/were), and the base of the main verb +ing.| Subject | was/were | base + ing |
|---|---|---|
| They | were | watching |
| Affirmative | ||
| She | was | reading |
| Negative | ||
| She | wasn’t | reading |
| Interrogative | ||
| Was | she | reading? |
| Interrogative negative | ||
| Wasn’t | she | reading? |
TO PLAY, PAST CONTINUOUS
| Affirmative | Negative | Interrogative |
|---|---|---|
| I was playing | I was not playing | Was I playing? |
| You were playing | You were not playing | Were you playing? |
| He was playing | He wasn’t playing | Was he playing? |
| We were playing | We weren’t playing | Were we playing? |
| They were playing | They weren’t playing | Were they playing? |


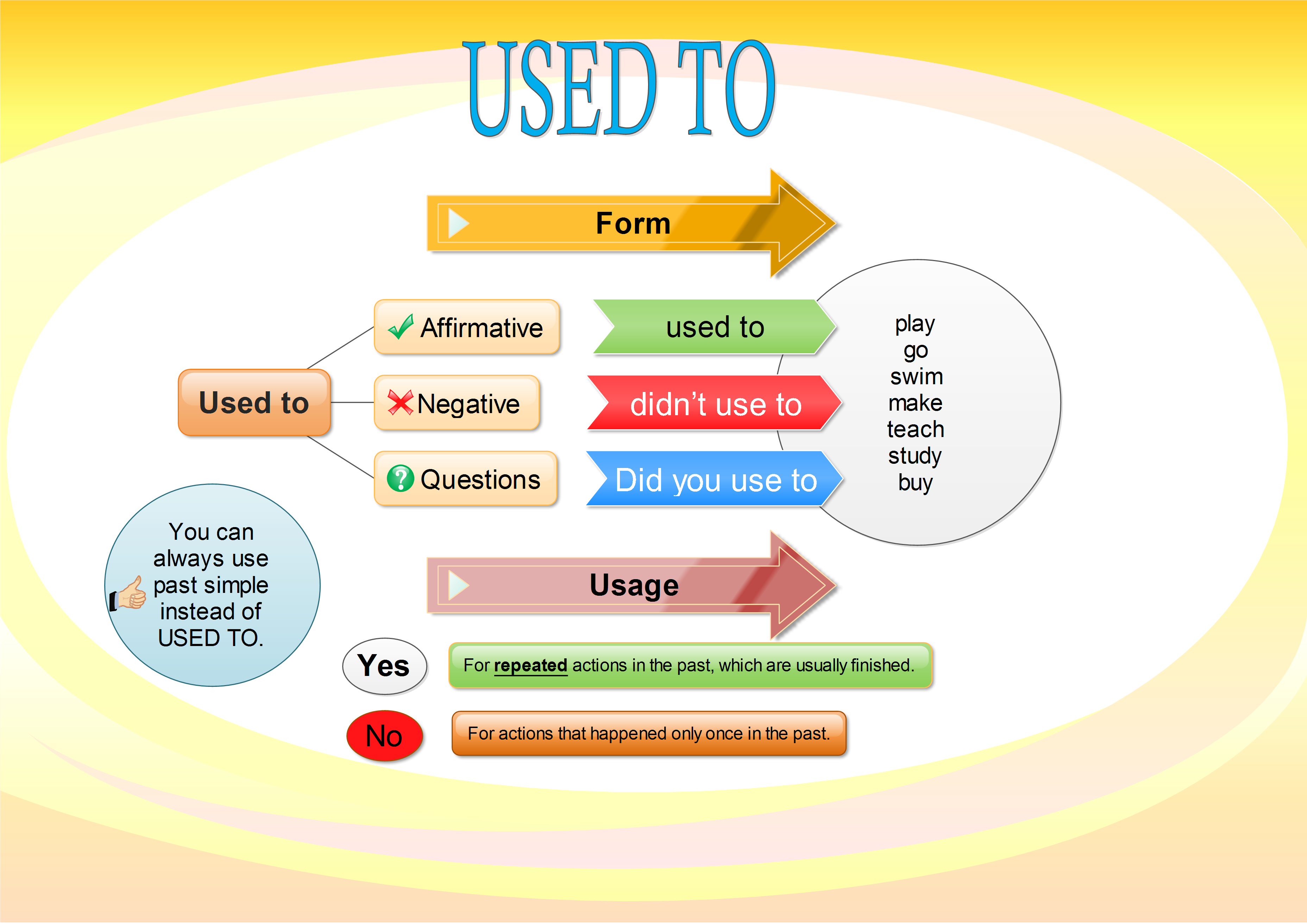
 “Used to” can also be used to talk about past facts or generalizations which are no longer true.
“Used to” can also be used to talk about past facts or generalizations which are no longer true.



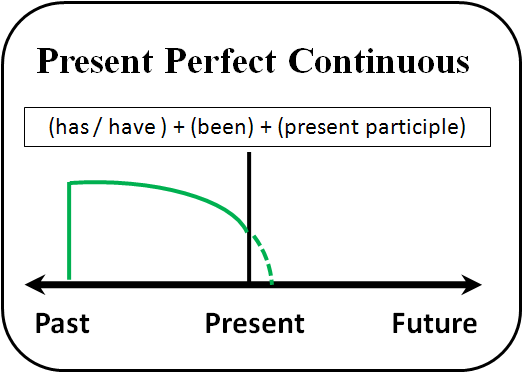

 We use the Present Perfect Continuous to show that something started in the past and has continued up until now. “For five minutes,” “for two weeks,” and “since Tuesday” are all durations which can be used with the Present Perfect Continuous.
We use the Present Perfect Continuous to show that something started in the past and has continued up until now. “For five minutes,” “for two weeks,” and “since Tuesday” are all durations which can be used with the Present Perfect Continuous.

 We use the Present Perfect to say that an action happened at an unspecified time before now. The exact time is not important. You CANNOT use the Present Perfect with specific time expressions such as: yesterday, one year ago, last week, when I was a child, when I lived in Japan, at that moment, that day, one day, etc. We CAN use the Present Perfect with unspecific expressions such as: ever, never, once, many times, several times, before, so far, already, yet, etc.
We use the Present Perfect to say that an action happened at an unspecified time before now. The exact time is not important. You CANNOT use the Present Perfect with specific time expressions such as: yesterday, one year ago, last week, when I was a child, when I lived in Japan, at that moment, that day, one day, etc. We CAN use the Present Perfect with unspecific expressions such as: ever, never, once, many times, several times, before, so far, already, yet, etc.

 FORMING THE PRESENT PERFECT
FORMING THE PRESENT PERFECT
 ]]>
]]>




 Simple Present Tense
Simple Present Tense
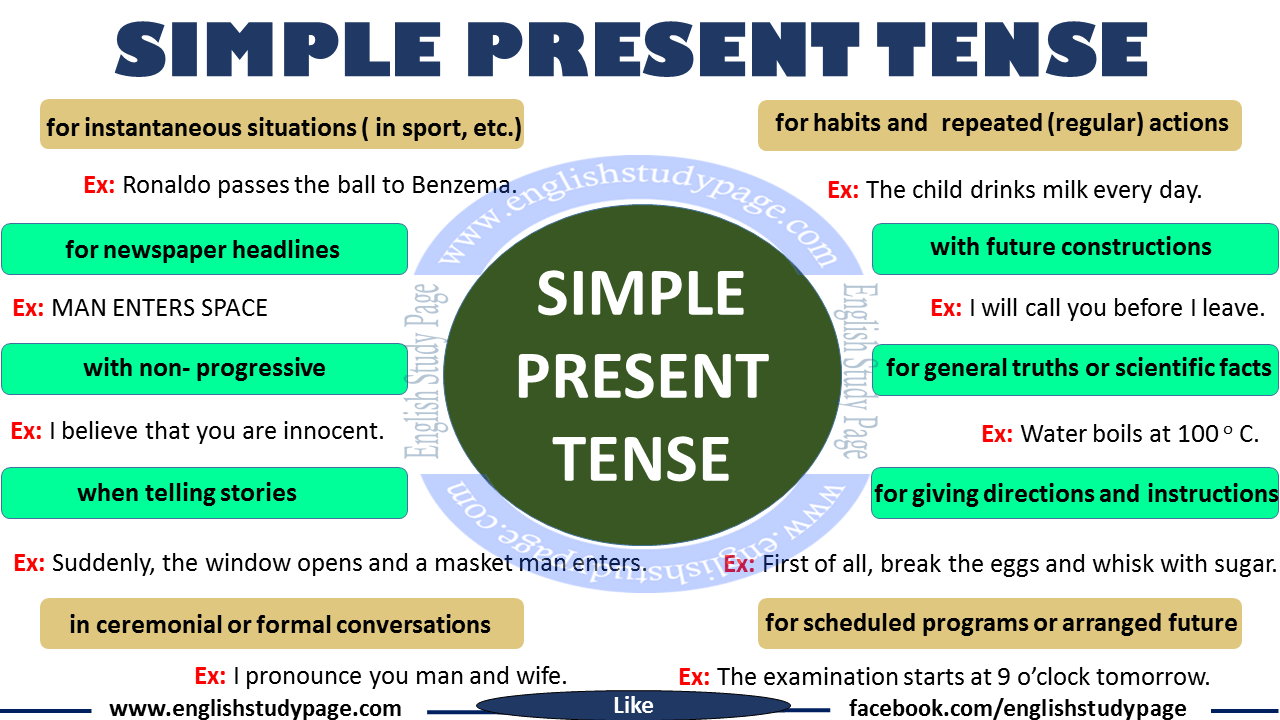
 FORMING THE SIMPLE PRESENT TENSE: TO THINK
FORMING THE SIMPLE PRESENT TENSE: TO THINK
.jpg)

 Swedish Subject and Object Pronouns
Swedish Subject and Object Pronouns
 The only case of nouns that is used in Swedish is the genitive (showing possession), and it is easily formed by adding an -s to the noun. This is comparable to adding -‘s in English to show possession. However, if the noun already ends in -s, then you add nothing (unlike English where we add -‘ or -‘s). Anders bok = Anders’s book
The only case of nouns that is used in Swedish is the genitive (showing possession), and it is easily formed by adding an -s to the noun. This is comparable to adding -‘s in English to show possession. However, if the noun already ends in -s, then you add nothing (unlike English where we add -‘ or -‘s). Anders bok = Anders’s book