The simple present tense is one of several forms of present tense in English. It is used to describe habits, unchanging situations, general truths, and fixed arrangements. The simple present tense is simple to form. Just use the base form of the verb: (I take, you take, we take, they take) The 3rd person singular takes an -s at the end. (he takes, she takes)
Simple Present Tense
In Simple Present, the action is simply mentioned and there is nothing being said about its completeness. It is used to talk about an action which happens on a regular basis.
POSITIVE STATEMENTS
| SUBJECT |
VERB |
REST OF THE SENTENCE |
| I |
study |
in Bal Bharti school. |
| You |
study |
in Bal Bharti school. |
| He |
studies |
in Bal Bharti school. |
| Mohan |
studies |
in Bal Bharti school. |
| The boy |
studies |
in Bal Bharti school. |
| She |
studies |
in Bal Bharti school. |
| Pooja |
studies |
in Bal Bharti school. |
| The girl |
studies |
in Bal Bharti school. |
| We |
study |
in Bal Bharti school. |
| You |
study |
in Bal Bharti school. |
| They |
study |
in Bal Bharti school. |
| The children |
study |
in Bal Bharti school. |
Notice how we use ‘study’ for the subjects I, You, We, You and They and we use ‘studies’ for the subjects ‘He’ and ‘She’.
NEGATIVE STATEMENTS
| SUBJECT |
DON’T (DO NOT) / DOESN’T (DOES NOT) |
VERB |
REST OF THE SENTENCE |
| I |
don’t |
play |
football. |
| You |
don’t |
play |
football. |
| He |
doesn’t |
play |
football. |
| Mohan |
doesn’t |
play |
football. |
| The boy |
doesn’t |
play |
football. |
| She |
doesn’t |
play |
football. |
| Pooja |
doesn’t |
play |
football. |
| The girl |
doesn’t |
play |
football. |
| We |
don’t |
play |
football. |
| You |
don’t |
play |
football. |
| They |
don’t |
play |
football. |
| The men |
don’t |
play |
football. |
Notice how we use ‘don’t’ for the subjects I, You, We, You and They
and we use ‘doesn’t’ for the subjects ‘He’ and ‘She’. The verb form remains the same for all subjects.
INTERROGATIVE STATEMENTS / QUESTIONS
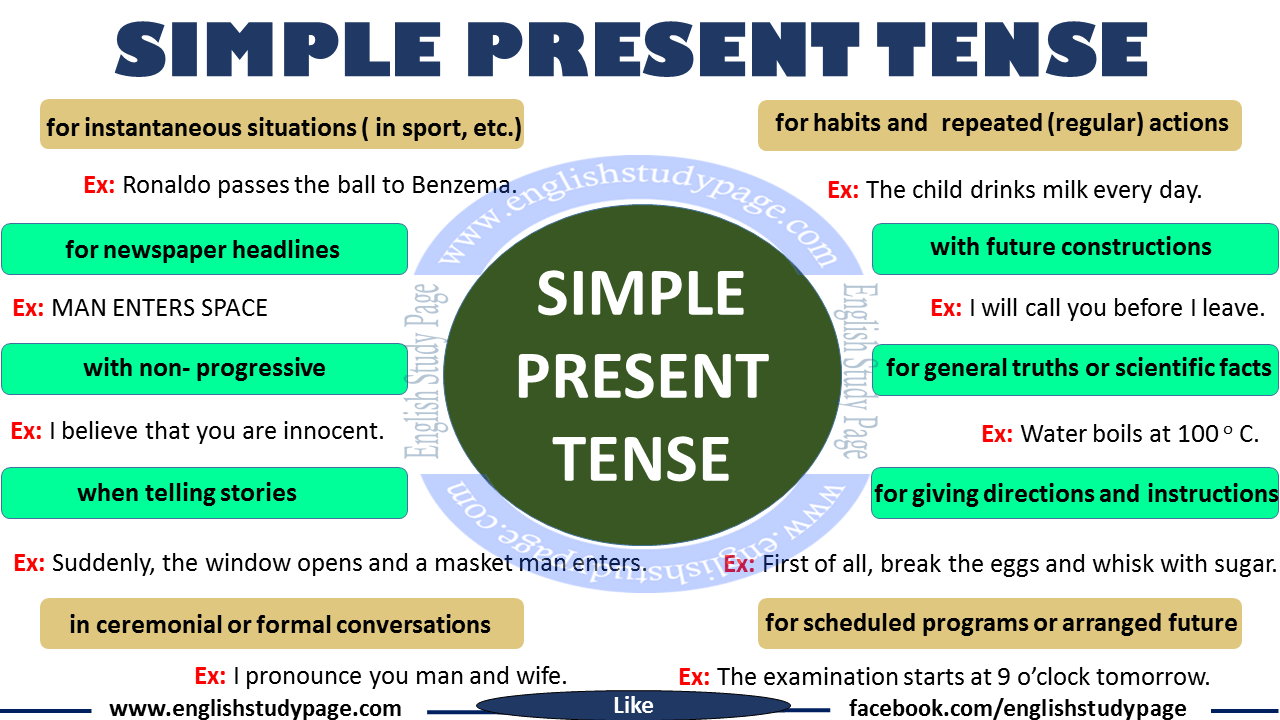
THE SIMPLE PRESENT TENSE IS USED:
- To express habits, general truths, repeated actions or unchanging situations, emotions and wishes:
I smoke (habit); I work in London (unchanging situation); London is a large city (general truth)
- To give instructions or directions:
You walk for two hundred meters, then you turn left.
- To express fixed arrangements, present or future:
Your exam starts at 09.00
- To express future time, after some conjunctions: after, when, before, as soon as, until:
He’ll give it to you when you come next Saturday.
Be careful! The simple present is not used to express actions happening now.
EXAMPLES
- For habits
He drinks tea at breakfast.
She only eats fish.
They watch television regularly.
- For repeated actions or events
We catch the bus every morning.
It rains every afternoon in the hot season.
They drive to Monaco every summer.
- For general truths
Water freezes at zero degrees.
The Earth revolves around the Sun.
Her mother is Peruvian.
- For instructions or directions
Open the packet and pour the contents into hot water.
You take the No.6 bus to Watney and then the No.10 to Bedford.
- For fixed arrangements
His mother arrives tomorrow.
Our holiday starts on the 26th March
- With future constructions
She’ll see you before she leaves.
We’ll give it to her when she arrives.
 FORMING THE SIMPLE PRESENT TENSE: TO THINK
FORMING THE SIMPLE PRESENT TENSE: TO THINK
| Affirmative |
Interrogative |
Negative |
| I think |
Do I think? |
I do not think |
| You think |
Do you think? |
You do not think |
| He thinks |
Does he think? |
He does not think |
| She thinks |
Does she think? |
She does not think |
| It thinks |
Does it think? |
It does not think |
| We think |
Do we think? |
We do not think. |
| They think |
Do they think? |
They do not think. |

NOTES ON THE SIMPLE PRESENT, THIRD PERSON SINGULAR
- In the third person singular the verb always ends in -s:
he wants, she needs, he gives, she thinks.
- Negative and question forms use DOES (= the third person of the auxiliary ‘DO’) + the infinitive of the verb.
He wants ice cream. Does he want strawberry? He does not want vanilla.
- Verbs ending in -y : the third person changes the -y to -ies:
fly –> flies, cry –> cries
Exception: if there is a vowel before the –y:
play –> plays, pray –> prays
- Add -es to verbs ending in:-ss, -x, -sh, -ch:
he passes, she catches, he fixes, it pushes
EXAMPLES
- He goes to school every morning.
- She understands English.
- It mixes the sand and the water.
- He tries very hard.
- She enjoys playing the piano.
 Simple Present Tense
Simple Present Tense
 FORMING THE SIMPLE PRESENT TENSE: TO THINK
FORMING THE SIMPLE PRESENT TENSE: TO THINK
