 Russian Pronouns
Russian Pronouns
These are the Russian pronouns that can be used as the subject of a sentence. (Known as the nominative case.)
Я – I
Ты – You (informal)
Он – He, It (m)
Она – She, It (f)
Оно – It (n)
Мы – We
Вы – You (formal, or plural)
Они – They
Вы is used as the formal singular “you”, and the plural “you” (slang: “yous” or “you all”) when talking to more than one person. Here are the Russian pronouns that can be used as the object of a sentence. (Known as the accusative case)Меня – Me
Тебя – You (informal)
Его – (“yevo”) – Him, It (m,n)
Её – Her, It (f)
Нас – Us
Вас – You (formal, or plural)
Их – Them
You should be familiar with using different pronouns for the subject and object of a sentence (“me” instead of “I”). Just remember that unlike English,Russian uses an extra version of the word “you”. You should memorise these pronouns.
Nouns and Gender
Russian nouns have three genders: Masculine, Feminine and Neuter.
You can see which gender the noun is by looking at the ending in the nominative case.
Masculine nouns end in consonants or й
EXAMPLES:
адрес – address
брат – brother
взрослый – adult
Feminine nouns end in –а, –я, or –ия
EXAMPLES:
книга – book
аллея – avenue
биология – biology
Neuter nouns end in –е, –о, or –ие
EXAMPLES:
животное – animal
лето – summer
курение – smoking
There are a few masculine nouns that end in –a/я, such as мужчина (man), дедушка(grandfather), дядя (uncle), or diminutive forms of masculine proper names, like Вася,Андрюша, and so on.
Neuter nouns ending in –о, –е or –и that are direct imports from foreign languages, such asкино, кафе or такси, do not decline (do not change the endings).


Personal Pronouns
These are Russian personal pronouns:
я (I)
ты (you – singular)
он (he)
она (she)
оно (it)
мы (we)
вы (you – plural), Вы (you – singular formal)
они (they)
In Russian, as in many other languages, ты is generally used among people who know each other very well. Otherwise, it is more appropriate to use formal вы. It is commonly capitalized in formal writing when used as a polite address “Вы“.
In Russian language, the personal pronoun determines the form of the verb in the present tense:
EXAMPLES:
Я делаю/строю (I am doing/building)
Ты делаешь/строишь (You are doing/building)
Он/она/оно делает/строит (He/she/it is doing/building)
Мы делаем/строим (We are doing/building)
Вы делаете/строите (You are doing/building)
Они делают/строят (They are doing/building)
Possessive Pronouns
| Personal Pronouns | Possessive pronouns | Translation |
| я | мой (Masculine) моя (Feminine) моё (Neuter) мои (Plural) | my/mine |
| ты | твой (Masculine) твоя (Feminine) твоё (Neuter) твои (Plural) | yours |
| он | его | his |
| она | её | her/hers |
| оно | его | its |
| мы | наш (Masculine) наша (Feminine) наше (Neuter) наши (Plural) | our/ours |
| вы | ваш (Masculine) ваша (Feminine) ваше (Neuter) ваши (Plural) | your/yours |
| они | их | their/theirs |
Это ваша квартира.
EXAMPLES:
Это мой дом (masculine singular). – It is my house.
Это ваша квартира (feminine singular). – It is your(plural) apartment


Possessive construction «У меня есть» (I have)
The idea of possession is very often expressed in Russian with the help of the construction
“У меня есть (I have)”.
у меня (есть)
у тебя (есть)
у него (есть)
у неё (есть)
у него (есть)
I have
you have
he has
she has
it has
у нас (есть)
у вас, у Вас (есть)
у них (есть)
we have
you (plural and formal) have
they have
Affirmative
Preposition у + pronoun in the Genitive case + есть+ noun in the Nominal case. The verb естьcan be omitted.
EXAMPLES:
У него есть машина. – He has a car.
У меня есть брат. – I have a brother.
У неё серые глаза. – She has grey eyes.
Negative
Preposition у + a pronoun in the Genitive case + нет + noun in the Genitive case.
EXAMPLES:
У меня нет времени. – I have no time.
У нас нет денег. – We have no money.
У вас нет компьютера́. – You don’t have a computer.
Interrogative
Preposition у + a pronoun in the Genitive case + есть* + noun in the Nominal case. The verbесть can be omitted.
EXAMPLES:
У тебя есть друзья? – Do you have friends?
У них есть билеты? – Do they have tickets?
Russian Possessive Pronouns
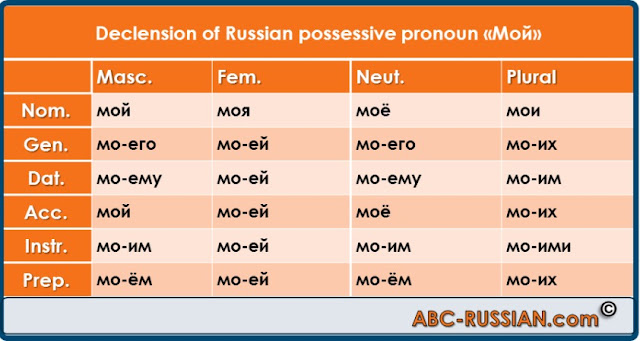
Possessive pronouns indicate who something belongs to. They may replace a person’s name in the sentence, “Ivan’s Book”. Words like “My, Your, Our, His, Her” in English. Please note that the genders indicated in the following tables refer to the gender of the noun that these pronouns modify. (ie the noun owned). For example in the phrase “My book”, you would use the 1st person (my) and feminise gender (book is feminine) (Моя). Don’t confuse this with the pronouns “his” and “her” (Его and Её).Singular possessive pronouns.
| 1st Person | 2nd Person | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Masc. | Fem. | Neut. | Plural | Masc. | Fem. | Neut. | Plural | |
| English | My, Mine | Your, Yours | ||||||
| Nominative Case | Мой | Моя | Моё | Мои | Твой | Твоя | Твоё | Твои |
| Accusative Case (animate) | Мой Моего | Мою | Моё | Мои Моих | Твой Твоего | Твою | Твоё | Твои Твоих |
| Genitive Case | Моего | Моей | Моего | Моих | Твоего | Твоей | Твоего | Твоих |
| Dative Case | Моему | Моей | Моему | Моим | Твоему | Твоей | Твоему | Твоим |
| Instrumental Case | Моим | Моей | Моим | Моими | Твоим | Твоей | Твоим | Твоими |
| Prepositional Case | Моём | Моей | Моём | Моих | Твоём | Твоей | Твоём | Твоих |
 Plural possessive pronouns.
Plural possessive pronouns.
| 1st Person | 2nd Person | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Masc. | Fem. | Neut. | Plural | Masc. | Fem. | Neut. | Plural | |
| English | Our | Your, Yours | ||||||
| Nominative Case | Наш | Наша | Наше | Наши | Ваш | Ваша | Ваше | Ваши |
| Accusative Case (animate) | Наш Нашего | Нашу | Наше | Наши Наших | Ваш Вашего | Вашу | Ваше | Ваши Ваших |
| Genitive Case | Нашего | Нашей | Нашего | Наших | Вашего | Вашей | Вашего | Ваших |
| Dative Case | Нашему | Нашей | Нашему | Нашим | Вашему | Вашей | Вашему | Вашим |
| Instrumental Case | Нашим | Нашей | Нашим | Нашими | Вашим | Вашей | Вашим | Вашими |
| Prepositional Case | Нашем | Нашей | Нашем | Наших | Вашем | Вашей | Вашем | Ваших |
Reflexive possessive pronoun свой
Apart from using possessive pronouns, to express the idea of possession Russians use the reflexive possessive pronoun свой. Depending on the context, it can mean “my”, “your”, “her”, “his” etc. It is used instead of possessive pronouns and refers back to the subject of the sentence. The form depends on the gender and number of the object.
| masculine | feminine | neuter | plural | |
| Nominative | свой | своя́ | своё | свои́ |
| Genitive | своего́ | свое́й | своего́ | свои́х |
| Dative | своему́ | свое́й | своему́ | свои́м |
| Accusative | своего́ | свою́ | своего́ | свои́х |
| Instrumental | свои́м | свое́й | свои́м | свои́ми |
| Prepositional | своём | свое́й | своём | свои́х |
EXAMPLES:
Я потерял свои заметки. – I lost my notes.
Он потерял свои заметки. – He lost his notes.
Мы потеряли свои заметки. – We lost our notes.
Заметки on monikossa, joten oikea muoto on свои.
Talking about 1st or 2d person, you can use the possessive pronouns, but it is more natural to use свой:
EXAMPLES:
Я люблю свой дом / Я люблю мой дом – I love my home.
Вы расскажете о своей поездке? / Вы расскажете о вашей поездке? – Will you tell about your trip?
Talking about 3d person, be sure to choose the right pronoun:
EXAMPLES:
Она продала свою квартиру – reflexive possessive pronoun – She sold her (own) apartment.
Она продала её квартиру – possessive pronoun – She sold her (someone else’s) apartment.
Note:
When talking about body parts, Russians most often omit possessive pronouns.
EXAMPLES:
Он сломал руку. – He broke his arm.
Она открыла глаза – She opened her eyes.
Russian Reflexive Pronouns
Personal Reflexive Pronoun “Себя” (-self) The Russian pronoun “Себя” means self. It is used when the pronoun is the same person or thing as the subject. Example “He talked about himself (Он говорил о себе)”. Himself is a reflexive pronoun.| English | Myself, himself, herself. |
| Nominative Case | —- |
| Accusative Case | Себя |
| Genitive Case | Себя |
| Dative Case | Себе |
| Instrumental Case | Себой |
| Prepositional Case | Себе |
Reflexive possessive pronoun “Свой”
The Russian pronoun “Свой” means “one’s own”. It replaces the normal possessive pronoun when it refers to the subject. Example “Ivan loves his (own) dog (Иван любит свою собаку)”. Unlike English, in Russian the reflexive is required in the 3rd person. If you were to use the normal possessive pronoun it would indicate the dog belongs to someone else. It is optional in the 1st and 2nd person but normally used if the subject is “Ты”.| Masc. | Fem. | Neut. | Plural | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| English | My own, his own, her own | |||
| Nominative Case | Свой | Своя | Своё | Свои |
| Accusative Case (animate) | Свой Своего | Свою | Своё | Свои Своих |
| Genitive Case | Своего | Своей | Своего | Своих |
| Dative Case | Своему | Своей | Своему | Своим |
| Instrumental Case | Своим | Своей | Своим | Своими |
| Prepositional Case | Своём | Своей | Своём | Своих |
Emphatic pronoun “Сам”
The Russian pronoun “Сам” is simply used to emphasise something. It translates to “myself, himself, herself” etc. It’s use is optional, it emphasises part of the sentence, rather than changing it’s meaning. Some examples could be: “I did it myself (Я сам сделал)”, “I will phone the president himself”.| Masc. | Fem. | Neut. | Plural | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| English | Myself, himself, herself | |||
| Nominative Case | Сам | Сама | Само | Сами |
| Accusative Case (animate) | Сам Самого | Саму | Само | Сами Самих |
| Genitive Case | Самого | Самой | Самого | Самих |
| Dative Case | Самому | Самой | Самому | Самим |
| Instrumental Case | Самим | Самой | Самим | Самими |
| Prepositional Case | Самом | Самой | Самом | Самих |
Russian Demonstrative Pronouns
Demonstrative pronouns are commonly used when you are pointing to something, or indicating what you are talking about with your body. “This” is used to indicate something close by, and “That” is used to indicate something not so close.This
| Masc. | Fem. | Neut. | Plural | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| English | This | |||
| Nominative Case | Этот | Эта | Это | Эти |
| Accusative Case (animate) | Этот Этого | Эту | Это | Эти Этих |
| Genitive Case | Этого | Этой | Этого | Этих |
| Dative Case | Этому | Этой | Этому | Этим |
| Instrumental Case | Этим | Этой | Этим | Этими |
| Prepositional Case | Этом | Этой | Этом | Этих |
That
| Masc. | Fem. | Neut. | Plural | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| English | That | |||
| Nominative Case | Тот | Та | То | Те |
| Accusative Case (animate) | Тот Того | Ту | То | Те Тех |
| Genitive Case | Того | Той | Того | Тех |
| Dative Case | Тому | Той | Тому | Тем |
| Instrumental Case | Тем | Той | Тем | Теми |
| Prepositional Case | Том | Той | Том | Тех |
Russian Determinative Pronouns
All
| Masc. | Fem. | Neut. | Plural | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| English | All, the whole | |||
| Nominative Case | Весь | Вся | Всё | Все |
| Accusative Case (animate) | Весь Всего | Всю | Всё | Все Всех |
| Genitive Case | Всего | Всей | Всего | Всех |
| Dative Case | Всему | Всей | Всему | Всем |
| Instrumental Case | Всем | Всей | Всем | Всеми |
| Prepositional Case | Всём | Всей | Всём | Всех |
Russian Interrogative Pronouns
Interrogative pronouns are used to ask questions. “What?” and “Who?” have cases based on there location in the sentence. For example you would use the prepositional to ask “About what?”. Example: “What are you talking about (О чём вы говорите?)”What?
| English | What |
| Nominative Case | Что |
| Accusative Case | Что |
| Genitive Case | Чего |
| Dative Case | Чему |
| Instrumental Case | Чем |
| Prepositional Case | Чём |
Russian Interrogative Pronouns
Interrogative pronouns are used to ask questions. “What?” and “Who?” have cases based on there location in the sentence. For example you would use the prepositional to ask “About what?”. Example: “What are you talking about (О чём вы говорите?)”What?
| English | What |
| Nominative Case | Что |
| Accusative Case | Что |
| Genitive Case | Чего |
| Dative Case | Чему |
| Instrumental Case | Чем |
| Prepositional Case | Чём |
Who?
| English | Who |
| Nominative Case | Кто |
| Accusative Case | Кого |
| Genitive Case | Кого |
| Dative Case | Кому |
| Instrumental Case | Кем |
| Prepositional Case | Ком |
