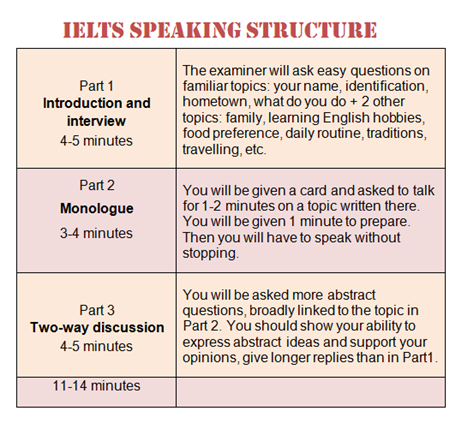
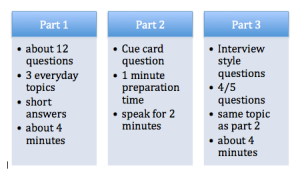
Mock IELTS tests and Practice Test for IELTS for Score Boosting
Part 1 – Introduction
Q. Good afternoon. My name is Kristina Pollock. Could I have your name please?
A. Good afternoon Madam. My name is Joseph Mark and my nick name is Mark.
Q. And your candidate number?
A. My candidate number is…..
Q. Thank you. Now could you tell me a little about yourself and where do you live?
A. Well, I’m Joseph Mark and I live at…. My father’s name is …. He is a Government service holder. My mother’s name is…. She is basically a housewife but sometimes she works at our shop. I’m 26 and I’ve finished my graduation from …. University. My major was Mathematics. I’ve got 2 brothers and a younger sister.
We live like a very happy family and my parents take great care of us. I’m doing a part time job at a local school as a Mathematics teacher. I’m planning to complete my M.Sc. from any reputed University of UK. My future plan is to teach in a college. I spend my leisure time surfing the internet and reading books. Sometimes I hang around with my friends on the lake shore.
The place I live now is really charming and I love to live there. It’s not noisy and busy like other cities and I have got many friends there. I am maintaining a personal blog and there I try to add a post every week. This is basically a technology and Math related blog.
Q. What are some of the nicest things about where you live?
A. The place where I live in is a clam area and is very neat and clean. You will find it naturally beautiful and the lakes, gardens, fountain, river, hill and the songs of birds will take your heart away. Whenever my friends from other cities come to visit my area, they become awestricken! Our area is indeed a beautiful place to live in. The people are very nice and friendly and you would be very pleased with their charming behaviours if you visit there.
The area is free of pollution as it not an industrial area and the fresh air would give a soothing feeling. The traffic on the road is good most of the time and you won’t have to worry about the public transportation as they are available around the clock. This area is famous for many historical sites and monuments like ……… and many tourists come to visit here every day. The tour guides are very nice and are maintained by Government.
There are many restaurants there and you can pick one of your delicious menus from there and I am sure you will never forget the taste! People in our area lead simple yet friendly lives and they make friends easily. The crime rate is pretty low and as a small town we know other members of our area.
I am sure if you visit our area once, you will simply love it.
Q. Are there any places of special interest I could visit in your home area?
A. The Gomez River and Roar Hills are two most beautiful places in our area. Thousands of tourists each month come to visit our area and these two places are main attractions for the tourists.
Apart from that, some monuments of famous politicians, poets and renowned persons in the Family Square is one of the main attractions and it is worth visiting. The hill hiking, swimming and fishing are three most popular activities among tourists and I would recommend those activities to you.
You will never get bored there and if you even slightly do, simply get yourself enrolled in the government managed tour plans for couple of days. This would give you a whole new chance to explore hills, rivers, forests and you would find challenges and enthralling experiences from there. Lastly, do not forget to taste our local foods and fruits.
Take the chance to visit our area and I am sure you would start recommending your friends after that.
 Q. Could you describe some of them for me?
A.
Q. Could you describe some of them for me?
A. The Gomez River is a long river that passes through our town. The water is crystal clear and you can see the fishes, corals and other objects inside it. The water is surprisingly warm and when you will look at it, you will be surprised to see all the fishes there. It is like a large aquarium.
The reflection of the sky gives it a heavenly look and many people go there for picnic and fishing there. In the evening children and parents play in the fields beside the river and you can find some newly constructed motels and restaurants there. Swimming in this river is a popular activity among local people and tourists in the summer season.
The Roar hill is another beautiful site in our area and it got its names from the roaring echo sound it creates. There are several hills there and they are over 300- 500 feet tall. The vista, illusionary sound of birds, the natural beauty and fountains give it a painted picture like looks. In the evening when the sun starts hiding behind the hills, people look at this out-of the-world scenery simply in amazement.
Q. What would be the best way for me to get there?
A. If you have private car with you, you can drive along the roads and reach there. From the city center, both of the destinations would be around 1 and half hour’s journey. Alternatively, you can take a public bus or hire a small car and reach there. The rent of the public transportation is fixed and you need not to pay any extra charge.
If you enroll with the tour service provider, they will manage the plan, route and based on your preference, you can either share a zip or can take a private car for rent. The later one is comparatively expensive.
Q. What sort of places could I stay at?
A. You can stay at a tourist motel near the hills or can rent a hotel room in the city center. If you are visiting your family members, then villa near the hill road would be better alternatives for you. Almost every tourist motel provides meals facility.
Q. Should I go at any special time of year?
A. Most of the tourists come to our area during the summer season and I would recommend you to visit during summer as well. There are lots of activities you can do during this period and you will find the beauty of our city at that time.
[ I see, this has all been very interesting.]
Part 2 – Cue Card
Topic:
Describe a problem that affects the environment in the area where you live.
You should say:
- what the problem is
- what causes it
- what people feel about the problem
and explain what you think could be done to solve it.
IELTS Speaking Part 2: IELTS Cue Card/ Candidate Task Card.
Describe a problem that affects the environment in the area where you live.
You should say:
- what the problem is
- what causes it
- what people feel about the problem
and explain what you think could be done to solve it.
Sample Answer:
There are so many problem that negatively affects the environment in our area and among them the highly density of population in my opinion is the most severe one. While in many countries, less than 100 people live in one square kilometer, we have got around thousands of people living in one square kilometer. Because of this high population in a small city, lots of problems are arising.
The expenditure to support living is quite high compared to the average earning of the people, a heavy traffic has become a common scenario in the roads and as a consequence, lots of time is killed every day. The lower economic people are not getting the proper education and hospital facility, crime has increase than ever, lots of unplanned and risky constructions have been established, the environment is getting polluted and seems like no one cares.
There are many reasons that caused this outburst of this mass population in our city and among them the most influential reason is the centralization of industry in this city. Most of the factory, offices and organizations are located in this city and people from all area of the country are coming here to find a living.
The unemployment in rural area is another reason why people are trying to stay here. The political reason not to take strict decisions on making equal opportunity in the country is another reason. The businesses and job opportunity attracts people to come and live here in this city.
People can feel the heat of this uncontrolled population and the problems are creating for that but they have little control over it. We all suffer from the problems and talk about it but I have not seen any big movement to solve this problem. On the other hand the political leaders who can take initiatives to lessen the problem are sometimes corrupted to take appropriate and honest steps.
There are lots of theories to solve this problem and seems like we all know about it. First of all decentralization should be done and industries and factories that can be moves to other areas should be moved. Proper education and job sectors should be ensured so that people can earn their living at their cities rather than coming here. Local government can be formed to support and improve each area of the country. Each local government should be able to invest and decide about the development projects in their area.
People naturally want to live in a better place where they can find the necessary infrastructure, daily needs and can earn a living. If that can be ensured throughout the country, this problem can be reduced.
Part 3 – Two-way discussion:
Q. What causes environmental problems?
Q. What should the government do to protect the environment?
Q. What should we do to protect the environment?
Q. What other measures can you think of to protect the environment?
Q. How should we educate children to protect environment?
Q. What’s the difference between the old and the young as regards environmental protection?
Similar Cue Card Topics
Your ability to talk about this Cue Card Topic would also enable you to talk about the following Cue Card Topics as well:
- Describe pollution in your city.
- Describe a problem you face in your city.
- Describe air or sound pollution in your city.
- Describe something you would like to change in your hometown.
Part 3 – Details Discussion
[Now let’s go to real life and you…..]
Q. Tell me, what do you think are the greatest problems facing your country at present?
A. Economic development issue, political instability, unemployment and healthcare are the major issues most of the people in my country face. In my opinion these are the most burning issues and the greatest problems we have in our country.
Q. And what has been done so far to solve these problems?
A. The government has taken many initiatives for the economic progress of our country. According to the statistics, we are indeed progressing. But I am not convinced with the reported statistics. I want to see the result, I want to feel it. The political instability seems like consuming most of our good will and energy. While major political parties should have worked together to help improve our economic conditions, sometimes their actions give me real doubt whether they are the type of leaders we need for our country!

On the positive sides, government has emphasized on ICT sector, has made the export process easier for business people, established many training institutes to enhance the skill of the rural people and those are all hopeful signs. Someday definitely we will see the progress.
Education, skill, foreign investment, job security etc. are also important areas where the government has invested a lot of money. The aim of this investment is to create a skilled and educated generation who would lead the economy and the country.
The healthcare section is still an expensive area for the mass people and the government’s initiatives for establishment of new hospitals, enrolling more doctors and nurses are in reality very little compared to the actual need.
Q. How successful would you say these measures have been?
A. These measures are successful to some extent but if I present it in figures, it would only few percentages than the actual progress we expect. For instance: more than three thousands hospitals are required throughout the country whereas only 45 hospitals have been established in the last one year.
Q. Do you think things are likely to get better or worse in the future?
A. We hope that the problem we have in our country would be resolved in next few years. The government and other organizations are working hard to address these issues and we are noticing some progress. So we can definitely be positive and wait for the glorious days when we won’t have those issues. This was an optimistic idea and I possess this positive idea about my country. But the greatest obstacle is the hunger for power and our political parties often create haphazard situation for the power. This is the single reason that can degrade the situation in the future.
Q. Is what you are going to study likely to be of any use to solve these problems?
A. I am going to finish my graduation majoring Computer Science and I am very positive that it would directly or indirectly help eradicate unemployment, economic progress issues to some extent that I have talked about. After finishing my education, I would establish a small software company and hopefully one day it would grow to be a large company where thousands of employees would work. The ICT sector also helps earning foreign remittance for a country and I would also contribute to enhance the foreign remittance for my country.
[Thank you very much. It’s been pleasant talking to you. I wish you success in your study program. Goodbye.]
 Formal Letters
After practicing a few informal letters, they can then practice a formal letter. In business letters, the date is usually written in numbers:
25.3.2010
The student would put his name and address on the top left-hand of the page, and the date on the right. He can also put the address on the right with the date beneath it. The heading would look somewhat like this:
Jan Schwartz
Hauptstrasse 56
92763 Stuttgart
Between the student’s address and the recipient’s address, there should be a few spaces:
Titles used are as follows:
Herrn (Mr)
Frau (Mr./Miss)
Familie (Family)
Herrn Doktor
Herrn Professor
It is usual in business letters to refer to the date of previous correspondence; so following the greeting, the student could begin his formal letter with something like:
Ihr Schreiben vom 15.April 2010
Let the student also practice another way of greeting. This is when the name of the recipient is known;in this case:
Sehr geehrter Herr Müller
Sehr geehrte Frau Weiss
He can also practice the form used when you do not know the person to whom you are writing:
Sehr geehrte Damen und Herren (Dear Sir or Madam)
A few more exercises in formal letters and your students will be well on their way towards receiving student help writing a letter in German, and understanding how to do it.
WE ALSO RECOMMEND…]]>
Formal Letters
After practicing a few informal letters, they can then practice a formal letter. In business letters, the date is usually written in numbers:
25.3.2010
The student would put his name and address on the top left-hand of the page, and the date on the right. He can also put the address on the right with the date beneath it. The heading would look somewhat like this:
Jan Schwartz
Hauptstrasse 56
92763 Stuttgart
Between the student’s address and the recipient’s address, there should be a few spaces:
Titles used are as follows:
Herrn (Mr)
Frau (Mr./Miss)
Familie (Family)
Herrn Doktor
Herrn Professor
It is usual in business letters to refer to the date of previous correspondence; so following the greeting, the student could begin his formal letter with something like:
Ihr Schreiben vom 15.April 2010
Let the student also practice another way of greeting. This is when the name of the recipient is known;in this case:
Sehr geehrter Herr Müller
Sehr geehrte Frau Weiss
He can also practice the form used when you do not know the person to whom you are writing:
Sehr geehrte Damen und Herren (Dear Sir or Madam)
A few more exercises in formal letters and your students will be well on their way towards receiving student help writing a letter in German, and understanding how to do it.
WE ALSO RECOMMEND…]]>








 On the positive sides, government has emphasized on ICT sector, has made the export process easier for business people, established many training institutes to enhance the skill of the rural people and those are all hopeful signs. Someday definitely we will see the progress.
Education, skill, foreign investment, job security etc. are also important areas where the government has invested a lot of money. The aim of this investment is to create a skilled and educated generation who would lead the economy and the country.
The healthcare section is still an expensive area for the mass people and the government’s initiatives for establishment of new hospitals, enrolling more doctors and nurses are in reality very little compared to the actual need.
Q. How successful would you say these measures have been?
A. These measures are successful to some extent but if I present it in figures, it would only few percentages than the actual progress we expect. For instance: more than three thousands hospitals are required throughout the country whereas only 45 hospitals have been established in the last one year.
Q. Do you think things are likely to get better or worse in the future?
A. We hope that the problem we have in our country would be resolved in next few years. The government and other organizations are working hard to address these issues and we are noticing some progress. So we can definitely be positive and wait for the glorious days when we won’t have those issues. This was an optimistic idea and I possess this positive idea about my country. But the greatest obstacle is the hunger for power and our political parties often create haphazard situation for the power. This is the single reason that can degrade the situation in the future.
Q. Is what you are going to study likely to be of any use to solve these problems?
A. I am going to finish my graduation majoring Computer Science and I am very positive that it would directly or indirectly help eradicate unemployment, economic progress issues to some extent that I have talked about. After finishing my education, I would establish a small software company and hopefully one day it would grow to be a large company where thousands of employees would work. The ICT sector also helps earning foreign remittance for a country and I would also contribute to enhance the foreign remittance for my country.
[Thank you very much. It’s been pleasant talking to you. I wish you success in your study program. Goodbye.]
On the positive sides, government has emphasized on ICT sector, has made the export process easier for business people, established many training institutes to enhance the skill of the rural people and those are all hopeful signs. Someday definitely we will see the progress.
Education, skill, foreign investment, job security etc. are also important areas where the government has invested a lot of money. The aim of this investment is to create a skilled and educated generation who would lead the economy and the country.
The healthcare section is still an expensive area for the mass people and the government’s initiatives for establishment of new hospitals, enrolling more doctors and nurses are in reality very little compared to the actual need.
Q. How successful would you say these measures have been?
A. These measures are successful to some extent but if I present it in figures, it would only few percentages than the actual progress we expect. For instance: more than three thousands hospitals are required throughout the country whereas only 45 hospitals have been established in the last one year.
Q. Do you think things are likely to get better or worse in the future?
A. We hope that the problem we have in our country would be resolved in next few years. The government and other organizations are working hard to address these issues and we are noticing some progress. So we can definitely be positive and wait for the glorious days when we won’t have those issues. This was an optimistic idea and I possess this positive idea about my country. But the greatest obstacle is the hunger for power and our political parties often create haphazard situation for the power. This is the single reason that can degrade the situation in the future.
Q. Is what you are going to study likely to be of any use to solve these problems?
A. I am going to finish my graduation majoring Computer Science and I am very positive that it would directly or indirectly help eradicate unemployment, economic progress issues to some extent that I have talked about. After finishing my education, I would establish a small software company and hopefully one day it would grow to be a large company where thousands of employees would work. The ICT sector also helps earning foreign remittance for a country and I would also contribute to enhance the foreign remittance for my country.
[Thank you very much. It’s been pleasant talking to you. I wish you success in your study program. Goodbye.]

 Take the three parts of this practice test one after another without a break to make your practice as realistic as possible.
Remember, you need to speak fluently, clearly and accurately. It is important to say as much as you can and to be spontaneous. Do not prepare answers in advance.
Record yourself if you can so that you can go back and check your performance.
Take the three parts of this practice test one after another without a break to make your practice as realistic as possible.
Remember, you need to speak fluently, clearly and accurately. It is important to say as much as you can and to be spontaneous. Do not prepare answers in advance.
Record yourself if you can so that you can go back and check your performance.







 We help students and professionals in and around Coimbatore and outlying areas to do their best in the IELTS Exams.`11
We also provide training for Cambridge Exams in Coimbatore
We help students and professionals in and around Coimbatore and outlying areas to do their best in the IELTS Exams.`11
We also provide training for Cambridge Exams in Coimbatore




 USE 1 Duration Before Something in the Future
USE 1 Duration Before Something in the Future

 The Future Perfect expresses the idea that something will occur before another action in the future. It can also show that something will happen before a specific time in the future.
The Future Perfect expresses the idea that something will occur before another action in the future. It can also show that something will happen before a specific time in the future.





 Use the Future Continuous to indicate that a longer action in the future will be interrupted by a shorter action in the future. Remember this can be a real interruption or just an interruption in time.
Use the Future Continuous to indicate that a longer action in the future will be interrupted by a shorter action in the future. Remember this can be a real interruption or just an interruption in time.

 When you use the Future Continuous with two actions in the same sentence, it expresses the idea that both actions will be happening at the same time. The actions are parallel.
When you use the Future Continuous with two actions in the same sentence, it expresses the idea that both actions will be happening at the same time. The actions are parallel.




