Simple, Compound and Complex Sentences :Part 2
A clause is a group of words having Subject and Predicate.
Model-1 :
In spite of, despite, not withstanding. – Simple
Though, although – Complex.
 Although it rained a lot, they enjoyed themselves. (Complex)
In spite of or Despite the rain, they enjoyed themselves. (Simple)
Although it rained a lot, they enjoyed themselves. (Complex)
In spite of or Despite the rain, they enjoyed themselves. (Simple)
 The food was very hot. We could not eat it. (Compound)
The food was so hot that we could not eat it. (Simple)
The food was too hot to eat. (Complex)
The food was very hot. We could not eat it. (Compound)
The food was so hot that we could not eat it. (Simple)
The food was too hot to eat. (Complex)
]]>
- If you study well, you will pass Subordinate Clause Main Clause
- Though he is poor, he is generous. Subordinate Clause Main Clause

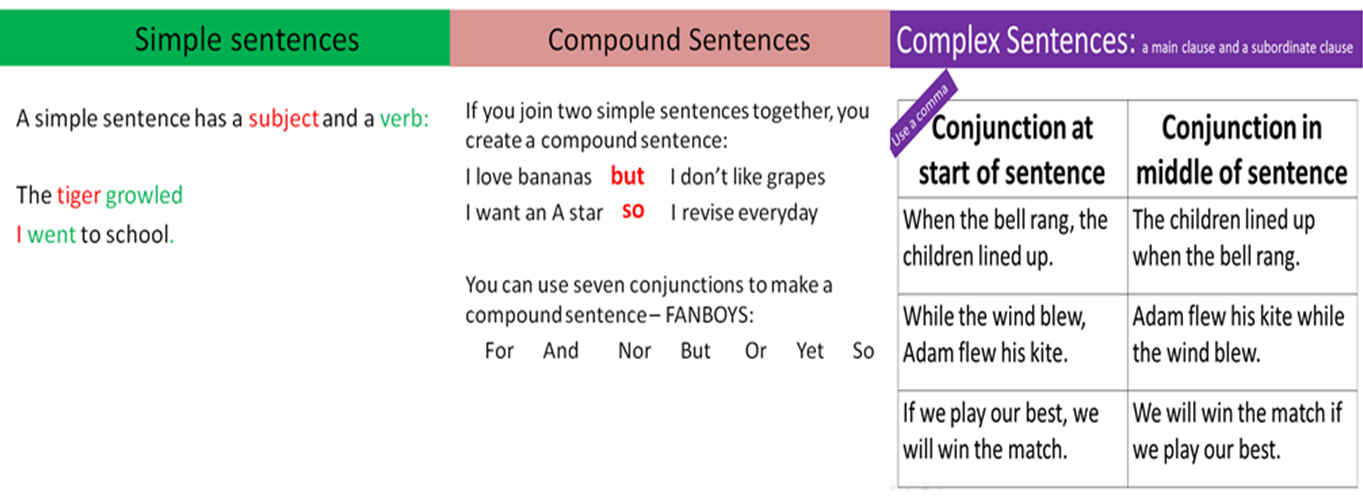
- A Simple Sentence contains one finite verb (i.e. a verb showing tense, person and number as : he goes; she went). That is to say, a simple sentence has one main clause, e.g. Seeing the wolf, the boy ran away. I’ve met him before.
- A Compound Sentence has two or more clauses. It may also have one or more subordinate clauses. e.g. The boy saw the wolf and ran away. I ran to the window and looked down into the street.
- A Complex Sentence has one main clause and one or more subordinate clauses. e.g. When the boy saw the wolf, he ran away. Before we went very far, we found that we had lost our way.
18 Rules :
| SIMPLE | COMPLEX | COMPOUND |
|---|---|---|
| After | After | and afterward |
| Before | Before | and before that |
| About | That | and about it |
| Till, untill | Till, untill | And till then |
| On | When | And then |
| During the period (time) of | While | and during that period (time) |
| Incase of / In the event of | If provided / provided that / should / were / supposing | And such a case / And in such and event |
| In case of … not | Unless | Must / else / or / otherwise |
| The manner of / The way of / The method of | How | And I know the method |
| Soon after / Immedicately after / Instantaneously after | As soon as / no sooner than | And immediately / and afterwards / and at once |
| For fear of | lest | And for that fear |
| The place of | where | And its place |
| The reason of / The cause | why | And + cause |
| Inspite of / Despite / on account of / not withstanding to | Though, Although / Eventhough / not withstanding that | But / yet / still / how ever / all the same / never the less |
| owing to / on account of / due to / because of | As, because since / for | And so / And therefore |
| During the whole length of / time of | As long as / so long as | And / during the length of time |
| Ever since | Ever since | And since then |
| Besides | As well as | Not only then… but also |
Examples :
| SIMPLE | COMPLEX | COMPOUND |
|---|---|---|
| Being tired, he went to bed. | As he was tired, he went to bed. | He was tired. He went to bed. |
| Having finished his work, he returned home. | After he had finished his work, he returned home. | He had finished his work. He returned home. |
| I saw a girl wiht blue eyes. | I saw a girl who had blue eyes. | I saw a girl. She had blue eyes. |
 Although it rained a lot, they enjoyed themselves. (Complex)
In spite of or Despite the rain, they enjoyed themselves. (Simple)
Although it rained a lot, they enjoyed themselves. (Complex)
In spite of or Despite the rain, they enjoyed themselves. (Simple)
- Thomas was a richman yet he led a simple life. (Compound)
- In spite of his being a richman. Thomas led a simple life. (Simple)
- Though Thomas was a richman, he led a simple life. (Complex)
- It rained heavily. The school was closed. (Compound)
- On account of heavy rain, the school was closed. (Simple)
- As it rained heavily, the school was closed. (Complex)
- He works hard and he will succeed. (Compound)
- In the event of his hard work, he will succeed. (Simple)
- If he works hard, he will succeed. (Complex)
 The food was very hot. We could not eat it. (Compound)
The food was so hot that we could not eat it. (Simple)
The food was too hot to eat. (Complex)
The food was very hot. We could not eat it. (Compound)
The food was so hot that we could not eat it. (Simple)
The food was too hot to eat. (Complex)
